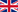
How PVD treatment works for thin film coating
|
Topics of the article: |
Physical Vapour Deposition, often abbreviated PVD, is a coating method for use with all types of materials, offering very strong adherence with very thin film layers.
Thin films are those with thicknesses on the order of a few microns or less: PVD can be used to create coatings just a few tenths or hundredths of a nanometre, and can generate different deposits in different layers. This is an atomic deposition process in which the coating metal is sublimed from a solid source, or evaporated from a liquid, into atoms or molecules. It is then transported in vapour form to the substrate to be coated, where it condenses and adheres very strongly.
The production of PVD (Physical Vapour Deposition) coatings using sputtering techniques calls for a continuous electric glow-discharge from a cathode, made from the material to be evaporated, and an anode, represented by the object to be coated, that is connected electrically to the deposition chamber and grounded for safety. The gas ions in which the discharge occurs collide with the cathode causing the ejection of atoms or molecules. The particles ejected from the cathode are in all effects in gas form and migrate toward the chamber and the substrate, where they condense, creating the coating.
The shapes and the compositions of the materials to be treated can vary from flat and regular, to highly complex geometries, like decorations or tools. Metals and plastics can be coated, improving the safety characteristics in terms of increased hardness, modified friction coefficient, and colour.
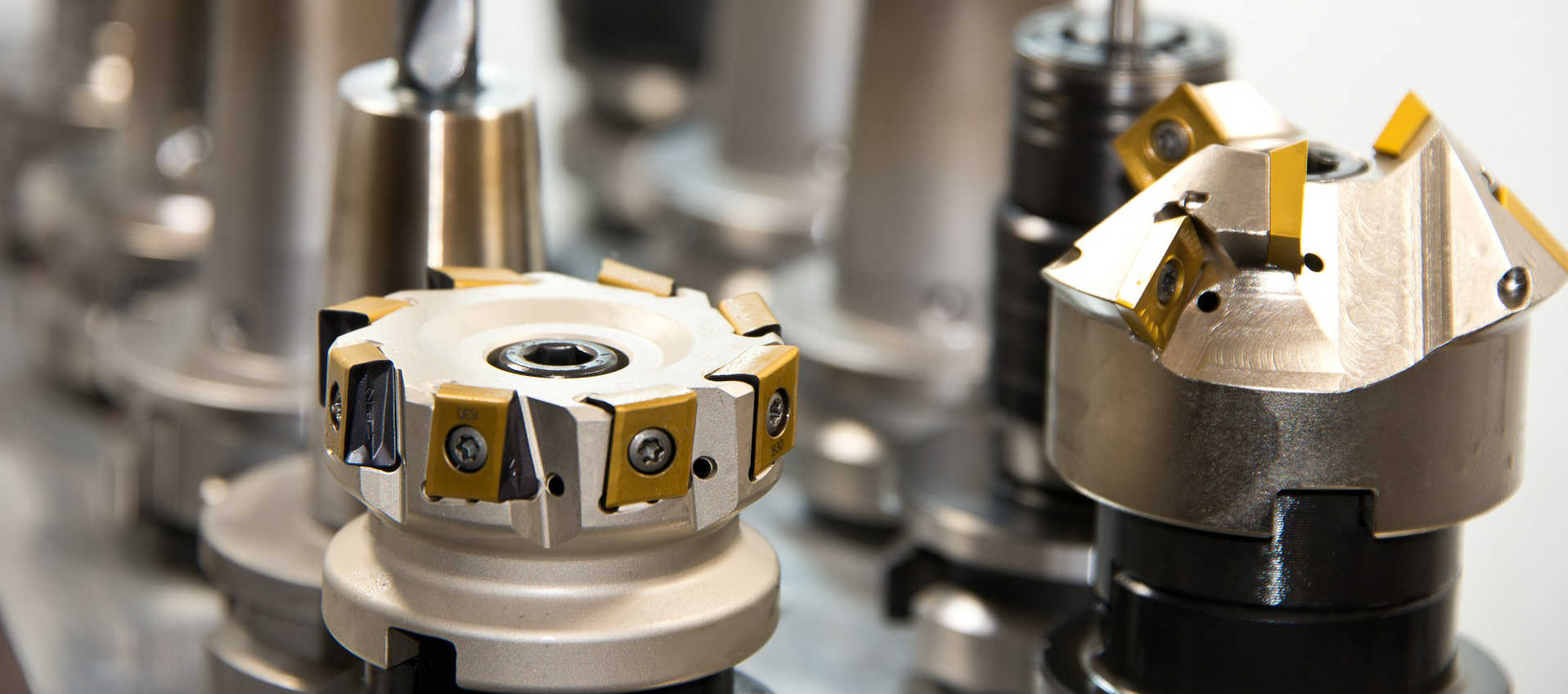
The advantages of the PVD treatment
1. Abrasion resistance due to hardness (up to 1000/2500 HV) can be obtained thanks to the density of the resulting surface
2. Inalterability to UV rays and resistance to solvents and corrosion
3. Impressive colour effects, like gold, silver, nickel, gun-barrel black, and many others.
4. Wide range of surface finished that range from brilliant glossy to satin, and even various degrees of opacity.
5. PVD coatings are hypoallergenic and resistant to sweat
In particular, PVD coating obtained with sputtering can be created using a wide variety of materials and substrates, for example (but not limited to):
- Titanium Nitrides - NiN
- Zirconium Nitrides - ZrN
- Titanium Carbon Nitrides - TiCN
- Zirconium Carbon Nitrides - ZrN
- Chromium Carbon Nitrides - CrCN
Titanium Nitride
Titanium Nitride is among the most common components used by the CM Group for PVD treatments. It is popular due to its hardness, chemical inertness, and for its golden colour, which makes it a natural replacement for gold in aesthetic-decorative coatings. Titanium Nitride PVD is used to harden and protect cutting and sliding surfaces, like drill bits or blades of industrial tools, or for decor, and as a non-toxic surface finish for medical prosthesis as well as for cutlery, plumbing fittings, and furnishings.
Based on the substrate and the surface finish, the titanium nitride coating has a friction coefficient between 0.4 and 0.6, and a hardness estimated to be equivalent to 85 on the Rockwell C scale.
Gold PVD coating
One of the most spectacular effects that can be obtained with physical vapour deposition is that applied to precious items, for example rings, chains, watch boxes, and bands. The finish provides an appearance very similar to that of solid gold.
In PVD treatment on jewellery, the technique allows the entire surface of the watch, and often the band, to be coated with a thin layer of titanium nitride, an extremely dense metal compound with excellent hardness.
This processing is performed under vacuum in controlled atmosphere. This guarantees the surfaces treated long-lasting protection against scratches, abrasions, and accidental dents to which wrist watches are inevitably subject. This coating is in fact as resistant as the sapphire, and is second in hardness only to the diamond.
In Titanium Nitride coatings, a layer of gold can also be added, that gives the piece treated the same brilliant, warm appearance as solid gold, as well as effective protection against corrosive agents like salt water, sweat, and pollution. It is a long-term guarantee against spots and oxidation.
Items subject to PVD are also used in the forks of motorcycles and bicycles to protect the wear surfaces, and in many cases the components of automobiles and industrial machinery.

PVD is ecological
Finally, it is a good idea to underline how the entire PVD process is innocuous for the environment. Under no phase of processing are polluting liquids or toxic waste produced that can poison our planet. The PVD process is safe, clean and eco-sustainable.
It is not toxic, and is even used to treat medical instruments, like scalpel and saw blades for orthopaedic use, where honing and lifetime are important, in implants and treatment of materials for bone prosthesis, especially for hips. It is even used for kitchen equipment, like cutlery, trays, and decor items for prolonged contact with people.
Antioxidant treatment of steel: PVD or electrolytic galvanisation?
The thin film deposition treatments of steel are often used in alternative to the classic electrolytic galvanization, which calls for the application of a surface coating of zinc using an electrolyte soak on a steel product, with the objective of protecting it from corrosion. Electrolytic galvanization is normally used when only corrosion protection is required, without the need for surface finish. For example, when treating chains or anchors for the nautical industry, or for certain needs in building on static materials, which as they do not have any moving or exposed parts, do not require a specific friction coefficient, hardness, or aesthetic finish.